The law requires new California residents to register their cars with the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) within 20 days of moving to California.
Here’s what you’ll need to register a vehicle in the Golden State – and how to do it right.
Not from out of state? We have a guide for general California vehicle registration too!
How to Register an Out-of-State Vehicle in California – 6 Steps
As a newcomer to California, you must establish residency and then make an appointment at the local
1. Fill Out an Application Registration Form
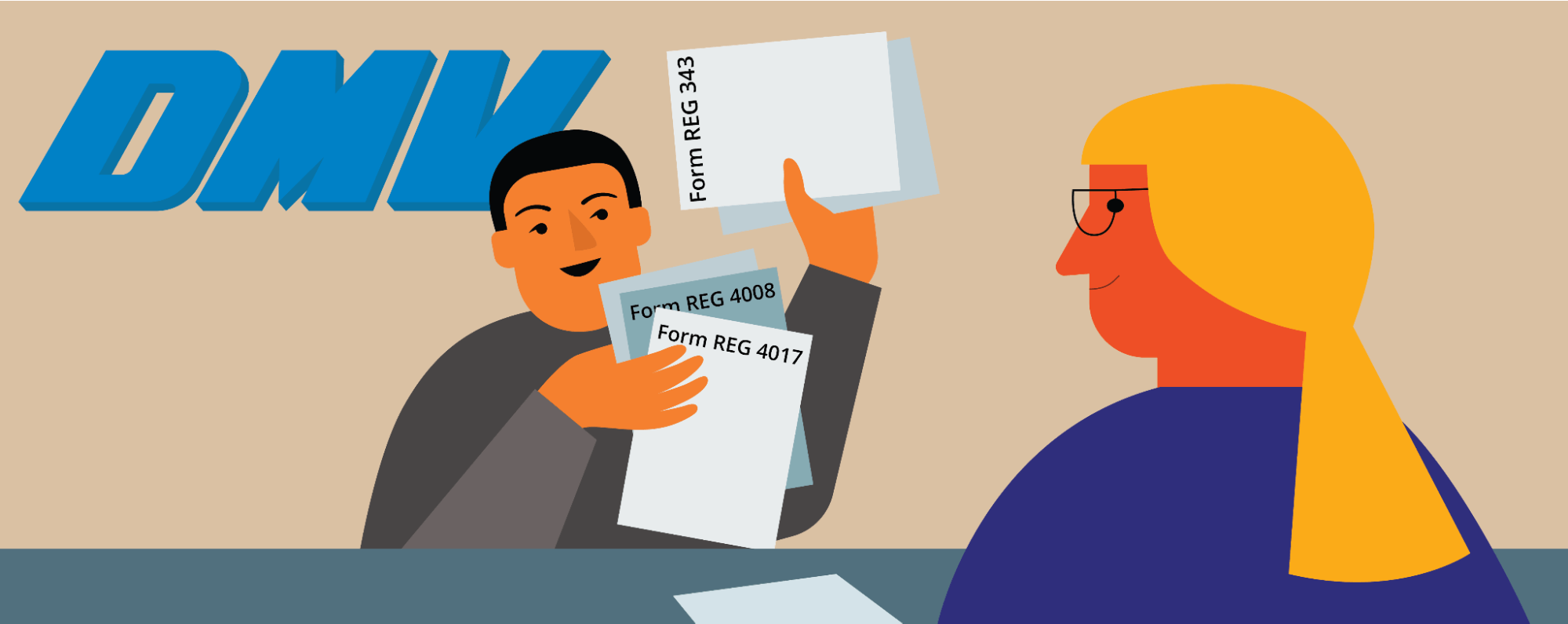
As a newcomer to California, you must establish residency and then make an appointment at the local DMV office. Fill out the forms depending on your vehicle and then bring them along with the other documents to your local DMV. You’ll need the following documents:
- Form REG 343 (for personal vehicles)
- Form REG 4017 (for trailers)
- Form REG 4008 (for commercial vehicles)
- Form REG 31 (Verification of Vehicle)
- Proof of insurance
- The last issued out-of-state title
- The car’s registration certificate
- A smog certificate (for certain types of vehicles)
To register an out-of-state leased vehicle in California, you must ask the leasing company to sign the registration form (REG 343). Alternatively, they may send you a notarized power of attorney that allows you to sign on their behalf.
Bring your out-of-state license plates, too. You can skip this step if the license plates are expired or must be returned to the state where they were issued.
Just remember that you have only 20 days to register your car after establishing residency.
Traffic school can help you keep a clean driving record, prevent insurance increases, and more!
2. Have Your Car’s Paperwork Ready
Find the car’s most recent out-of-state title and registration certificate, and make sure they’re complete and accurate. Check for any discrepancies with the out-of-state title, such as missing signatures, before submitting your application.
Any issues with these documents can lead to vehicle registration delays, resulting in penalty fees.
3. Buy Auto Insurance
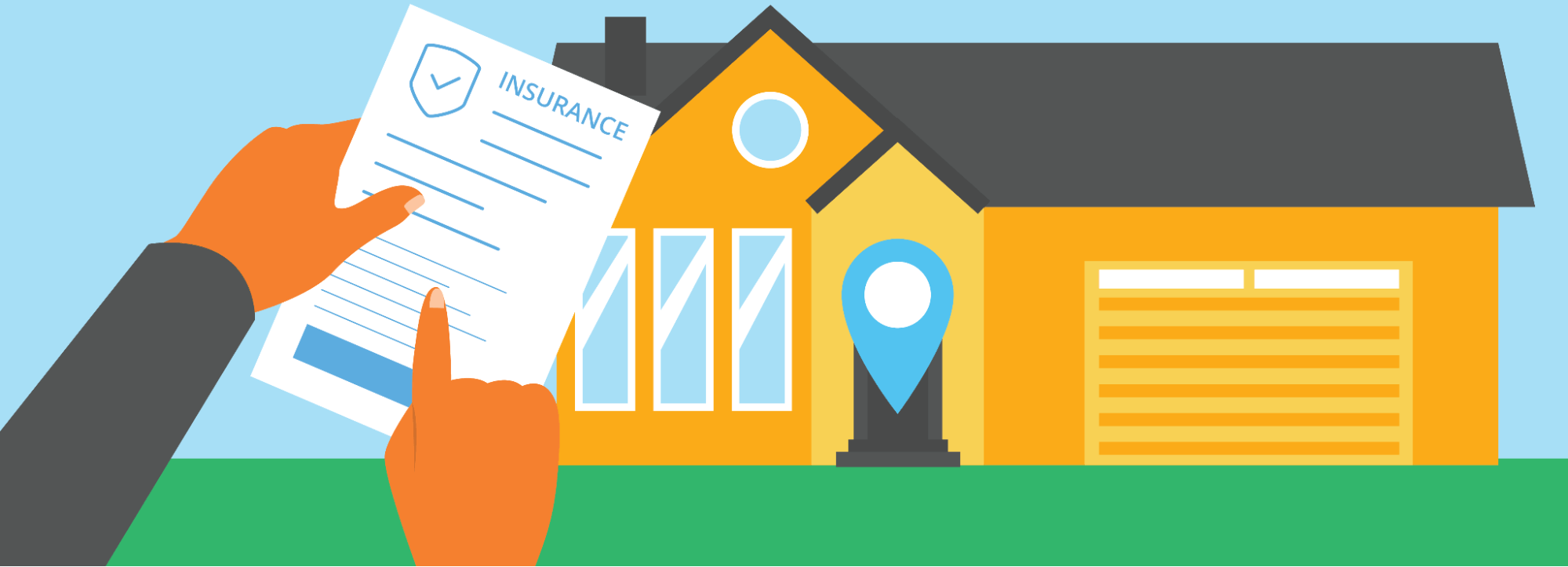
Purchase car insurance from a company based in California (ask about these hidden discounts!). Bring a copy of your insurance policy to the DMV when registering your vehicle.
4. Obtain a Smog Certificate
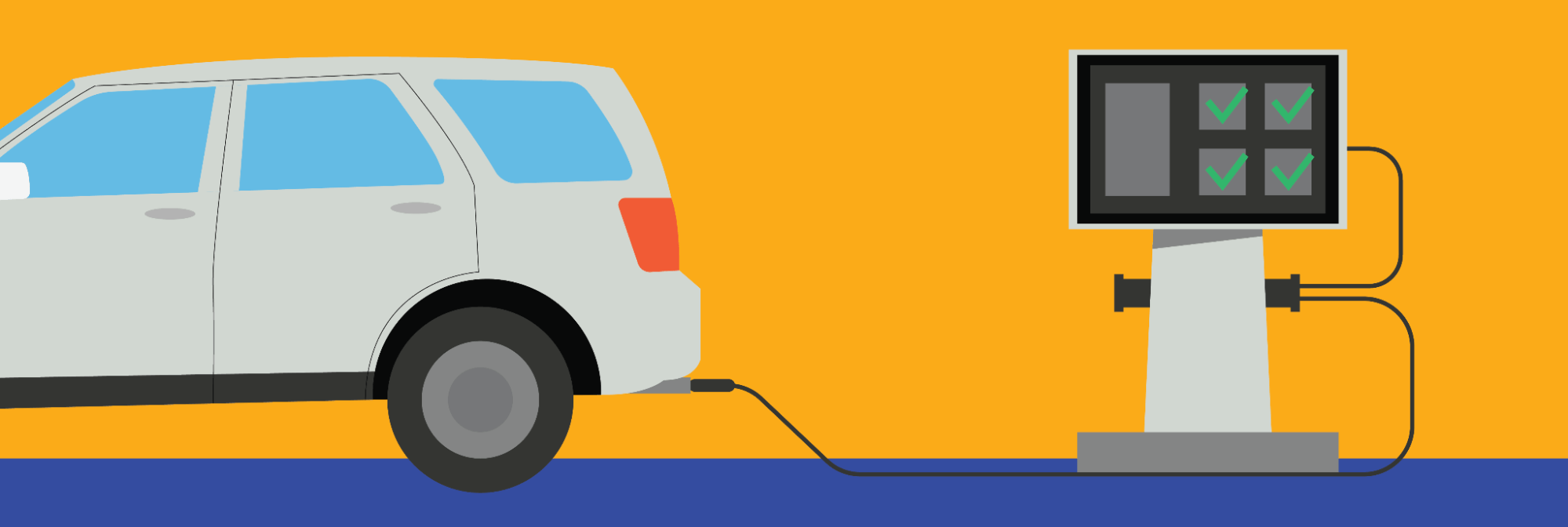
With a few exceptions, most newer vehicles must undergo a smog check before registration. This step is necessary for obtaining a smog certificate.
The California DMV requires a smog inspection for the following vehicles:
- Gasoline-powered cars produced after 1976
- Diesel-powered cars produced after 1998 with a gross vehicle weight of 14,000 pounds or less
- Any vehicle under 14,000 pounds powered by propane or natural gas
A smog inspections if not required for:
- Electric vehicles
- Gasoline-powered vehicles that are less than 8 model years old (you’ll pay an annual smog abatement fee instead)
- Motorcycles and trailers
- Diesel-powered vehicles with a model year of 1997 or older or those with a gross vehicle weight exceeding 14,000 pounds
- Natural gas vehicles weighing more than 14,000 pounds
Note that if you’re buying an older vehicle, a new law, Assembly Bill 1263, aims to establish a centralized testing network for vehicles from 1995 and older to improve the effectiveness of emissions testing on older vehicles.
If everything looks right, you’ll get a smog certificate. But if your car fails the smog test (about 14% of cars assessed in roadside checks failed in 2024), you’ll need to have it repaired to reduce its emissions.
Generally, a well-maintained vehicle should pass the smog check. Take these steps to increase your chances of passing on the first try:
- Do an oil change (if necessary)
- Clear your check engine light (if it’s on)
- Get a new gas cap if your vehicle is over five years old
- Check the exhaust system for leaks
- Change the car air filter (if necessary)
- Service the battery
- Flush the cooling system
Next, search for a DMV-approved smog check station in your area and book an appointment. Note that some stations can perform pre-inspections so you can identify and fix any issues that could cause your car to fail the emissions test.
5. Get Your Vehicle Verified
One of the documents you must have on hand is Form REG 31 (Verification of Vehicle), which will be completed by the DMV after inspecting your car.
Vehicle verifications are mandatory for most cars registered out-of-state. It is designed to ensure the car meets emissions standards and prevent theft and fraud by matching the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) to the owner’s documentation. This process involves a physical inspection of the car, during which a DMV employee (or other authorized parties) will check the following:
- VIN location
- Engine number
- Odometer mileage reading
- Ownership documents
- U.S. Federal Certification Label
- Emission label
The information on the registration application has to match what’s on the car. For example, your vehicle’s engine number must be the same as the one on the title or registration.
6. Pay the Registration Fees
The cost of vehicle registration starts at $74, which includes an alternative fuel/technology fee of $3. However, you may have to pay additional fees and taxes, depending on your circumstances. Vehicle registration fees depend on the city or county where you live and several other factors, including:
- Your car’s purchase price or declared value
- Car engine type (gas, diesel, or electric)
- Gross vehicle weight (GVW)
- Type of vehicle (e.g., passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, off-highway vehicles, or trailers)
- Other considerations (e.g., special license plates)
To get an estimate, use the DMV’s vehicle registration fee calculator for new residents. This should give you an idea of what you can expect to pay.
Pay the registration fees within 20 days of their due date, even if you don’t have all the necessary documents. The due date may vary based on a number of factors, such as when you established residency or when your out-of-state registration expires.
Failure to pay on time will result in penalty fees, as shown below:
| If payment is late | Penalty |
|---|---|
| One year or less | -40% of the vehicle license fee due for that year. -40% of the weight fee due for that year (if any). |
| More than one year – two years | -80% of the vehicle license fee due for that year. -80% of the weight fee due for that year (if any). |
| More than two years | -160% of the vehicle license fee due for that year. -160% of the weight fee due for that year (if any). |
Once these steps are completed, you’ll get your California registration card and license plates.
Other Taxes and Fees
Someone who bought a car in a state that doesn’t collect sales tax must pay those taxes after registering the vehicle in California unless the car was purchased more than one year prior.
The same applies to those who received the car as a gift or bought it from an out-of-state dealership (in which case the sales tax is usually included in the price).
Sales tax in California is 7.25% but can go up to 10% in some counties.
So, if you bought a $50,000 car from Delaware, Montana, or another state that doesn’t charge sales tax, you’ll pay $3,625 to $5,000 right off the bat when you bring it to California – in addition to registration fees and other charges, such as:
- County-specific fees
- California Highway Patrol (CHP) fee: $32
- Zero-emission vehicle parking fee: $17
- Smog abatement feet: $20
- Off-highway vehicle (OHV) fee: $33
- Non-resident service fee: $27
7. Get a California Driver’s License
You don’t need a California driver’s license to register your car with the state, but you must obtain one within 10 days of becoming a resident. If your job requires driving, you’ll have to get your California license immediately after moving.
You must also renew your California driver’s license every five years or more often, such as when changing your home address.
For more information, see our guide on how to switch a driver’s license from state to state.
For California Residents Bringing a Vehicle from Out of State
The above regulations apply to new residents who bring their cars to California. However, there are a couple of situations where you may need to register an out-of-state vehicle. These include:
- You live in California and bought your car from a dealership in another state. In such cases, the dealership will handle the paperwork. It may also give you license plates, collect sales tax, and pay it to your state.
- You live in California and purchase a car from a private out-of-state seller (not a dealership.) In this scenario, you will need to register the car in California within 20 days of purchase. You may or may not need a smog check depending on the car’s age. Otherwise, all the steps you follow will be the same as for those establishing residency in California.
- You have leased an out-of-state vehicle in California. In this scenario, you must ask the leasing company to sign the registration form (REG 343). Alternatively, they may send you a notarized power of attorney that allows you to sign on their behalf.
When You Need Out-of-State Vehicle Registration in California
If you’re a new resident, you have 20 days from the day you establish residency in California to register an out-of-state vehicle. If you’re a non-resident but plan to operate your vehicle in California for an extended period, you may be required to register it too. Let’s take a look.
For California Residents
You’re considered a resident of California and must register your vehicle with the state if:
- You work in California and pay income taxes in the state
- You rent or buy a home in California and use it as your permanent address
- You claim tax exemptions on a home in the state
- You register to vote in the California elections
- You’ve spent more than nine months in California
California defines residency as having a permanent home in the state. However, your residency status is determined based on several factors, with the length of your stay and where you have your closest connections being the most important.
According to Section 4000.4 of the California Vehicle Code, any vehicle based in California or primarily used on California highways must be registered with the state.
But, according to Section 6700, you are not required to register your car in California until you get a job or establish residency here, whichever occurs first.
These regulations don’t apply to students and military members, their spouses, children, or other close relatives.
For Students and Military Personnel
Out-of-state vehicle registration rules for students and military personnel located in California are a bit different because in most cases they are not considered residents. Here’s an overview.
Out-of-State Students:
Nonresident students attending California educational institutions are generally not required to register their out-of-state vehicles in California, provided:
- The vehicle is registered in the student’s home state.
- The student maintains full-time enrollment status.
- The vehicle is primarily used for personal transportation and not for commercial purposes.
Military Personnel:
Active-duty military members stationed in California may be exempt from registering their out-of-state vehicles if:
- The vehicle is registered in the service member’s home state.
- The service member is in California on military orders.
- The vehicle is not used in a trade or business.
To claim this exemption, military personnel should complete the Nonresident Military Exemption Statement (Form REG 5045) and carry it in the vehicle.
Both military personnel and students must have insurance that meets California’s minimum liability requirements.
What Happens If I Don’t Register My Out-of-State Car in California?
Driving an out-of-state car in California without registering it within 20 days of moving is illegal, and, in some cases, it can be classified as a misdemeanor.
Potential penalties include:
- Vehicle impoundment
- A base fine of up to $1,000 plus court and administration fees
- Jail time (less common)
- Penalty fees of 40-160% of the vehicle license fee (VLF) due for that year
- Penalty fees of 40-160% of the weight fee you were required to pay that year (if applicable)
Register Your Out-of-State Car in California
Registering an out-of-state car in California isn’t that difficult if you know what documents are needed. But since each case is different, consider reaching out to your local DMV office for more information.
Remember to apply for a state driver’s license within 10 days of moving to avoid fines and penalty fees. A valid California driver’s license will allow you to attend traffic school in the state and keep points off your record.
At Best Online Traffic School, you can study online from any device and finish the course in just two or three hours. Plus, you can take the final exam as many times as you need and pay only when you pass.
FAQs about Out-of-State Vehicle Registration in California
Want to know more about registering an out-of-state vehicle in California? Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions.
How long can you drive in California with an out-of-state registration?
You can drive an out-of-state car in California for 20 days after getting a job or establishing residency here, whichever comes first. If you are a California resident and purchase a car from out of state, you will also have 20 days to register it in California.
Do I need to change my license plate when I move to California?
Yes, you do. Any vehicle registered in the Golden State needs California license plates.
Can I live in California and have a car registered in another state?
If you’re a California resident, you can have your car registered in California AND another state. However, you may not drive a car that is registered in another state, but not in California.
Do I need proof of insurance to register my car in California?
When you register a vehicle in California, you must show proof of insurance. The policy must be purchased from an insurance carrier licensed in California.
How can I register an out-of-state car in California without a title?
The vehicle title serves as proof of ownership and, therefore, it’s necessary for registering your car in California or any other state, for that matter. If you have lost the title, you may request a copy from the state where it was issued. The same applies if the title has been stolen.
