When was the last time you checked your California driving record?
Also known as a California motor vehicle record (MVR), this document provides a comprehensive overview of your driving history. Employers, insurance providers, and other third parties can access it to assess your driving behavior and the risks associated with it.
Here’s how to request a copy from the DMV, what to look for, and how to resolve some of the key issues you might find.
Traffic school can help you keep a clean driving record, prevent insurance increases, and more!
How to Check Your California Driving Record
California drivers can request three types of driving records, depending on how they plan to use them.

- Unofficial driving record: This is a non-certified record you can access online through the California DMV website. It summarizes your driving history, including traffic violations, accidents, and license suspensions. The document is primarily used for personal reference or to check for errors and accuracy.
- Official driving record: This is a more formal record that can be obtained in-person or by mail. It provides the same information as the unofficial record, but may include more detailed historical information. Employers, insurance companies, or other third parties may request it to check your driving history.
- Certified driving record: This is when the official driving record is signed and stamped by the California DMV. It provides the same information as the official record but is used for legal proceedings, such as court cases or insurance claims.
There are three ways you can obtain your California DMV driving record: online, in person, or by mail. Here’s what you should know about each option.
Request Your California Driving Record Online
- Go to the California DMV website and visit Vehicle of Driver’s Records Requests.
- Click “Start driver’s record request.”
- Fill out the form.
- Enter your billing information to pay the fee.
- You will be able to download and print your record immediately.
Request Your California Driving Record in Person
- Find a local California DMV office near you.
- Make an appointment or visit the office during normal business hours.
- Bring your driver’s license or identification card with you.
- Request the type of driving record you want to order, and pay the fee.
- You’ll receive your official or unofficial record at the end of your visit.
Order Your Driving Record by Mail
- Download and print the “Request for Driver Record” form from the California DMV website.
- Fill out and sign the form.
- Choose the type of driving record you want to order. You can opt for a certified record at the top of the form.
- Include a check or money order for the fee, made payable to the California DMV.
- Mail the completed form and payment to the address listed on the form.
- You will receive an unofficial record within 7-10 business days and an official record within 10-15 business days.
Processing times may be longer during peak seasons or due to unforeseen circumstances. It’s always best to check with the DMV beforehand.
How Much Does It Cost to Check Your Driving Record?
The fees for obtaining your California DMV driving record vary from $2 to $8. What you’ll pay depends on the delivery method and type of record.
| UNOFFICIAL RECORDS | CERTIFIED RECORDS | |
|---|---|---|
| Online | $2 | $8 |
| In-person | $5 | $5 |
| By mail | $5 | $8 |
Additional fees may apply for expedited processing, as well as for requesting a record that requires certification or further research.
What’s in a California Driving Record?
A California driving record includes your name, address, and other personal data. It also contains information related to your driving behavior, such as fines, demerit points, and traffic tickets.
The most important sections include:
- Your personal details
- Driver’s license classification
- Driver’s license status
- Traffic violations
- Accidents
- DUI or DWI convictions
- Demerit points
- Suspensions or revocations
- Commercial driver’s license (CDL) information
Why Your Driving Record Matters
Your driving record may be accessed by employers, insurance companies, law enforcement and government agencies, and the courts. It may come into play when you are trying to:
- Find work
- Get into college
- Rent a car
- Adopt a child
- Hold public office
- Become a volunteer
If you’ve been charged with traffic violations – especially more serious offenses, such as DUIs or reckless driving – issues on your driving record could make you appear irresponsible or negligent and hurt your chances of employment.
Given these aspects, it makes sense to check your driving record at least once a year to understand what it contains – and look for errors that could be corrected.
How to Interpret Your Driving Record
Reading and understanding a driving record in California can be confusing due to the use of codes, abbreviations, and point systems. Here’s what to look for.
Review Your Personal Information
This section includes your name, date of birth, driver’s license number, and other identifying information. Make sure all the data is accurate and matches your records.
Check Your Driver’s License Status
The driving record will indicate whether your license is valid, suspended, or revoked. If your license is suspended or revoked, this document will state the reason behind it.
Look for Violations
Your California driving record will list all the traffic offenses you have been charged with, including moving and non-moving violations.
Each traffic offense will have a code or abbreviation associated with it, which can be found on the DMV website or in the California Vehicle Code. You can also search for any codes you find to discover what they mean. Take the time to review this information and understand what it means. You can also check out some of the common traffic misdemeanors and infractions and how they can impact your driving.
Check for Accidents
Your driving record will list any accidents you have been involved in while behind the wheel, including their date, location, and severity.
Look for Errors
Check for inaccuracies or errors, such as duplicate entries or points that should have been removed due to time passing. You can request to have incorrect information removed by completing a Report of Incorrect Record Form.
Check Your Point Count
California’s point system, also known as the Negligent Operator Treatment System (NOTS), assigns points to your driving record for each traffic violation you receive.
The number of points assigned depends on the severity of the violation; for example, a parking ticket carries no points, an infraction (like a speeding ticket or failure to yield) carries one point, and a serious driving offense (like reckless driving) carries two or more points.
Getting multiple points within set time periods can result in action from the DMV. It’s important to understand how many points are on your license and how that may impact you.
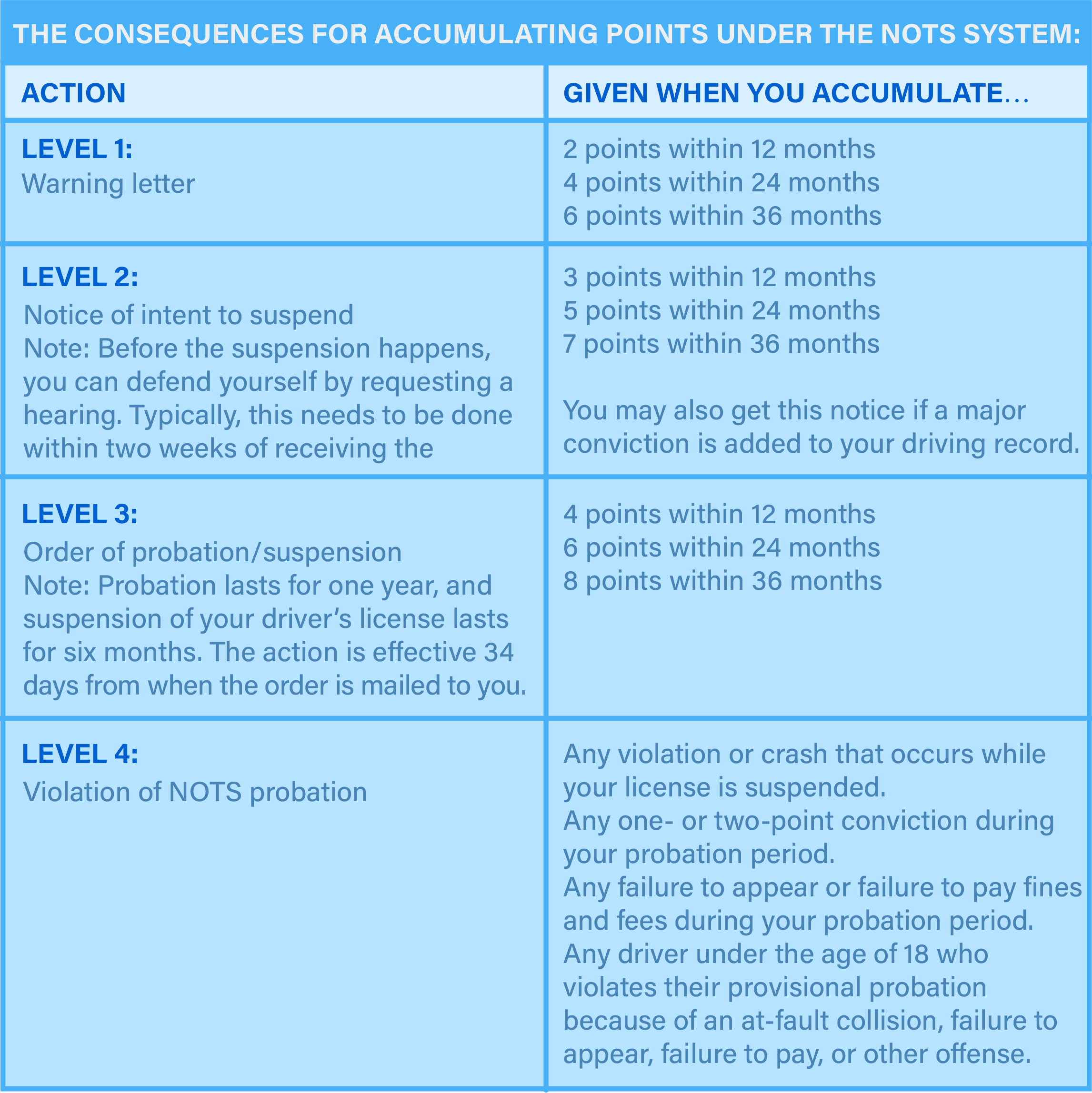
How to Remove Violations and Points from a Driving Record
A poor driving record can affect nearly every aspect of your life. Here are some of the steps you can take to clean up your driving record.
Remove Points from Your License

In California, it’s not possible to remove points from your license if you’re convicted of a violation that carries points. The points stay on your driving record for a set amount of time.
However, you can mask one point, meaning it won’t appear on any driving records shared with insurance companies. This can help keep your premiums from going up after a ticket or infraction. It will also be easier to qualify for a good driver discount.
To mask a point, you need to get permission from the court to attend a DMV-approved traffic school. Upon completion, the school will send your records to the DMV and one point will be masked from your driver’s license.
Dispute Any Inaccuracies or Errors
If you find errors on your driving record, you can request to have them corrected. The sooner you do it, the better.
Here’s how to proceed in each case.
Correcting Inaccurate Traffic Violations and Convictions
- Complete and submit the Driver License Record Correction Request (Form DL 207) to the California DMV.
- Submit any supporting documents you have to prove you weren’t convicted of the violation. The DMV will typically require a Court Abstract/Document Error (Form DL 157) and a signed or certified letter from the court (on an official letterhead).
- Mail the Correction Request and applicable documents to the address shown on your Correction Request form.
Correcting Inaccurate Traffic Accidents
- Complete and submit a Traffic Accident Record Correction Request (Form DL 208) to the DMV
- Submit any documents that prove the accident information is incorrect, such as the original traffic accident report. You can get these from the law enforcement agency that investigated the event.
- Mail the Correction Request and applicable documents to the address shown on your Correction Request form.
Appealing a License Suspension or Revocation
If you received a notice of suspension or revocation of your driver’s license, you can request a hearing to dispute the action within 10 days of receiving the suspension or revocation notice.
You can request a hearing by contacting the DMV Driver Safety Office. If you get a hearing, you will need to have evidence that supports your case. You can choose to represent yourself or hire an attorney.
Petitioning for Expungement of Driving-Related Convictions
If your driver’s record includes criminal convictions like a DUI, it is possible to petition the court to have that offense expunged. This will render the offense invisible to certain entities, although it may still be visible to law enforcement or the courts. If you want to pursue this option, you should consult with an attorney. Learn more in How Much Does a Traffic Lawyer Cost? (And When to Hire One.)
Final Thoughts
There are lots of good reasons to check your California driving record.
Perhaps a potential employer or your auto insurance provider requested this document. Or maybe you want to use it as evidence in legal proceedings.
In any of these cases, you can order a copy of your driving record from the California DMV. Once you know what it contains, you can decide on the next steps, such as attending traffic school to mask one point from your license.
With Best Online Traffic School, you can complete the course on your own time, from any device. The best part is, you don’t have to pay until you pass.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. Start traffic school for free today.
FAQs about California Driving Records
Looking for more information? Here are the answers to some frequently asked questions.
How to remove violations from a driving record in California?
If you’ve been charged with a traffic violation, you may or may not be able to remove it from your license. It all comes down to its type and severity.
Based on these factors, you may need to:
• Attend a DMV-approved traffic school
• Submit a Driver License Record Correction Request to the California DMV
• Submit a Traffic Accident Record Correction Request
• Appeal a driver’s license suspension or revocation
Are California driving records public?
Your DMV information is not publicly available. California has strict laws on who can access your driving record, and under what circumstances.
As you learned above, you can request your own driving record. So can authorized third parties, such as employers and insurance companies. Your driving record could also be requested by the courts to be used in legal proceedings.
How do I print my driving record in California?
Create a MyDMV account to get a copy of your driving record. Then pay a $2 fee to download and print the document.
How long does California keep driving records?
The California DMV will store the information on your driver’s record for up to 10 years or longer. The time frame depends on the traffic violations you’ve been charged with.
For example, a DUI conviction will stay on your record for 10 years. Most moving violations, such as following too closely, will be cleared after 39 months.
How to check if you have traffic tickets in California?
Depending on your circumstances, there are several ways to check if you have traffic tickets in California:
• Request a copy of your driving record from the California DMV;
• Check the website of the county court that issued your ticket. You may be able to search for unpaid tickets by entering your driver’s license number.
• Call or visit the traffic court where you suspect the ticket was issued.
• Check your mail or email for court notices.
How can I clean my driving record in California?
You can mask one point from your license by completing a traffic school course. If you’ve been charged with a more serious offense, you may need to:
• Wait for the violation to expire
• Contest the ticket in court
• Request a record correction
To make request a correction, complete and submit one of the following to the DMV:
• Driver License Record Correction Request (for traffic violations)
• Traffic Accident Record Correction Request (for traffic accidents)
Can I get my California driving record for free?
No, you may not. However, you can request an unofficial copy of your driver’s record online for only $2.
